Industrial robots can improve productivity, safety, and time efficiency in various industries. They can perform repetitive tasks quickly and accurately and can work 24/7 without fatigue. The use of robots in manufacturing and other industrial operations is called Industrial Robotics. These advanced robots perform tasks that were done by humans in the past in a traditional way. These robots are designed to make hard or complex tasks easy and automate processes like 3d printing. Robots in industries increase productivity and enhance performance and efficiency.
The concept of industrial robotics started in the early 20th century when many advanced mechanical devices were used in manufacturing.
The real shape of robotics in industrial regions appeared in the 1960s when the first industrial robot was introduced. This robot was developed by George Devol and Joseph Engelberger. After this industrial robotics became advanced and more advanced, integrated with different technologies, and transformed the whole industries across the world.
Industry plays a vital role in economics. Industrial robotics changes the traditional ways and methods which take a lot of time, improve precision, and achieve higher levels of productivity.
As technology continues to advance, the impact of robotics in various industries becomes more pronounced, reshaping the way goods are produced and services are delivered.
Types of Industrial Robots
There are different types of robots used in industries according to the type of task.
Articulated Robots
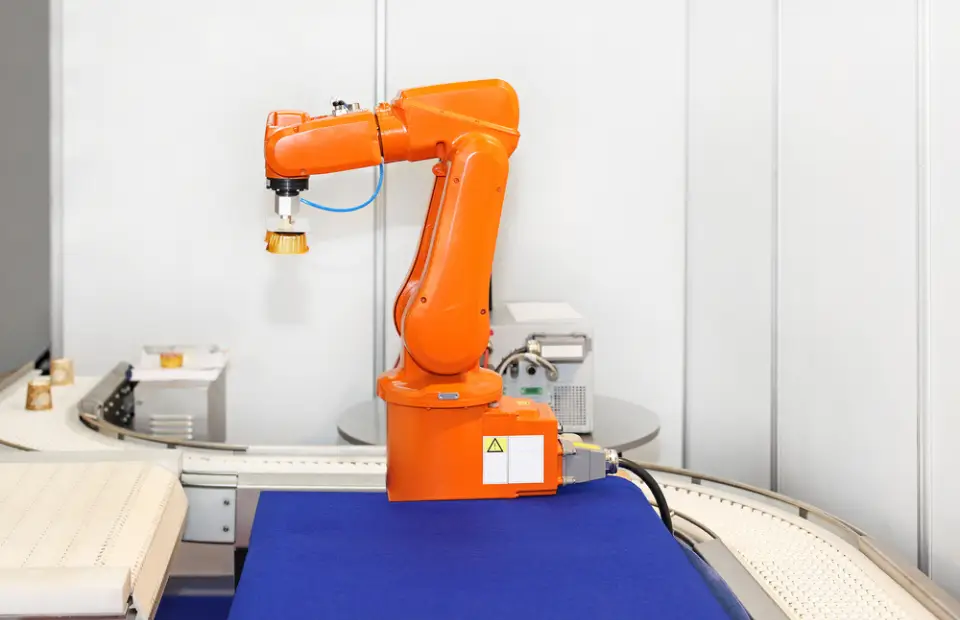

Articulated robots are versatile machines with rotary joints, that mimic the flexibility and range of motion of the human arm. These robots are suited for a variety of tasks due to their unique structure. Articulated robots are used in welding, painting, assembly, and material handling. Their ability to work with multiple axes makes them ideal for complex tasks in diverse manufacturing environments.
| Features | Multi-jointed design with rotary joints for flexibility in movement. |
| Advantages | High flexibility for complex tasks, wide range of motion, suitable for various applications in manufacturing. |
| Limitations | Complex programming requires a large workspace and a higher initial cost. |
Cartesian Robots

Cartesian Robots also known as gantry robots, move in straight lines along three axes. Their design simplifies programming and control. These robots are suitable for applications requiring precision and repeatability. These robots are used in tasks that demand accuracy, such as pick-and-place operations in assembly lines and tasks involving large workspaces.
| Features | Rectangular coordinate system for precise linear movements along three axes. |
| Advantages | Simple programming, high precision, well-suited for pick-and-place applications. |
| Limitations | Limited flexibility, may require larger workspace, less efficient for tasks with multiple orientations. |
SCARA Robots
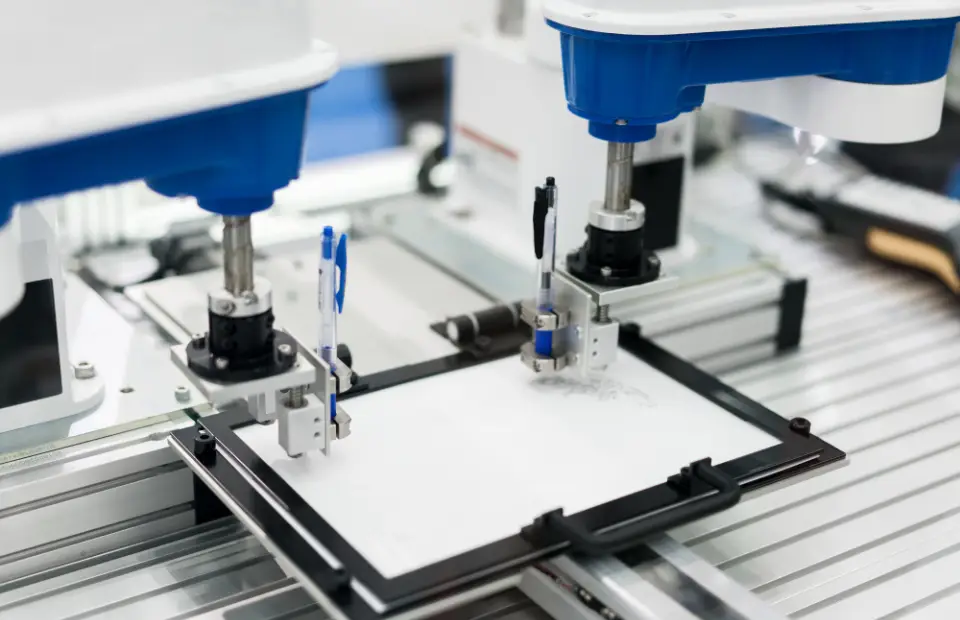

SCARA is abbreviated as Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm. These robots are commonly used in assembly processes that require high speed and precision, such as electronics manufacturing. SCARA robots enhance efficiency in assembly lines by rapidly and accurately placing components. Their design minimizes vibrations, contributing to the precision required in delicate tasks.
| Features | Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm with rotational and translational joints. |
| Advantages | Fast and precise, suitable for assembly tasks, compact design, and efficient use of workspace. |
| Limitations | Limited reach, less flexibility compared to articulated robots, higher initial cost. |
Delta Robots
Delta robots have parallel-link structures. These robots are used in high-speed applications like packaging and pick-and-place operations in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Their fast speed is so adorable so they are mostly used in applications where items need to be swiftly and accurately moved from one location to another.
| Features | Parallel robot with three arms connected to a common base, providing high speed and precision. |
| Advantages | Very fast and precise in high-speed applications, suitable for pick-and-place tasks, high payload capacity. |
| Limitations | Limited in terms of reach, complex kinematics, and higher cost. |
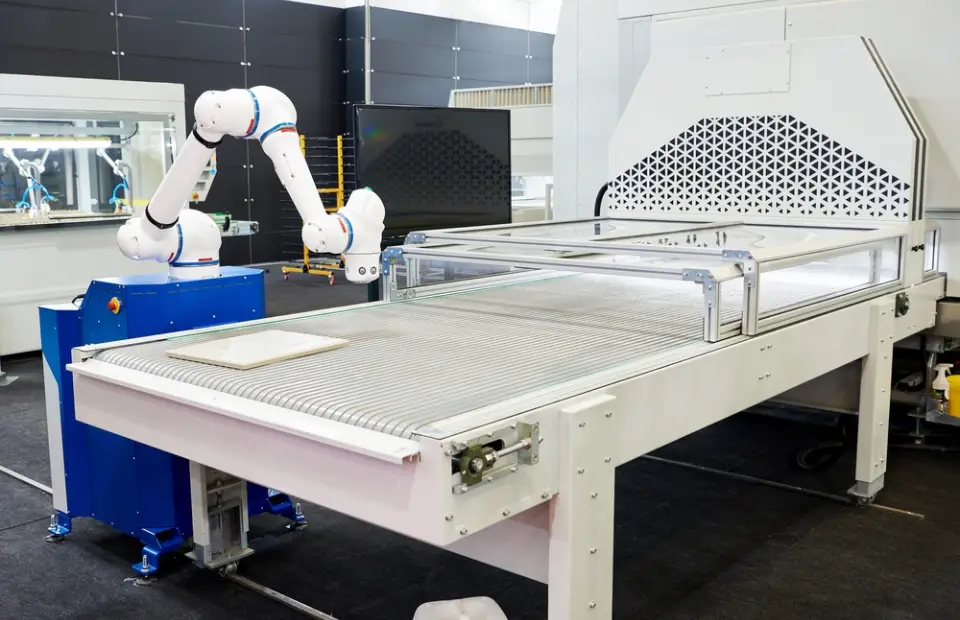
Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
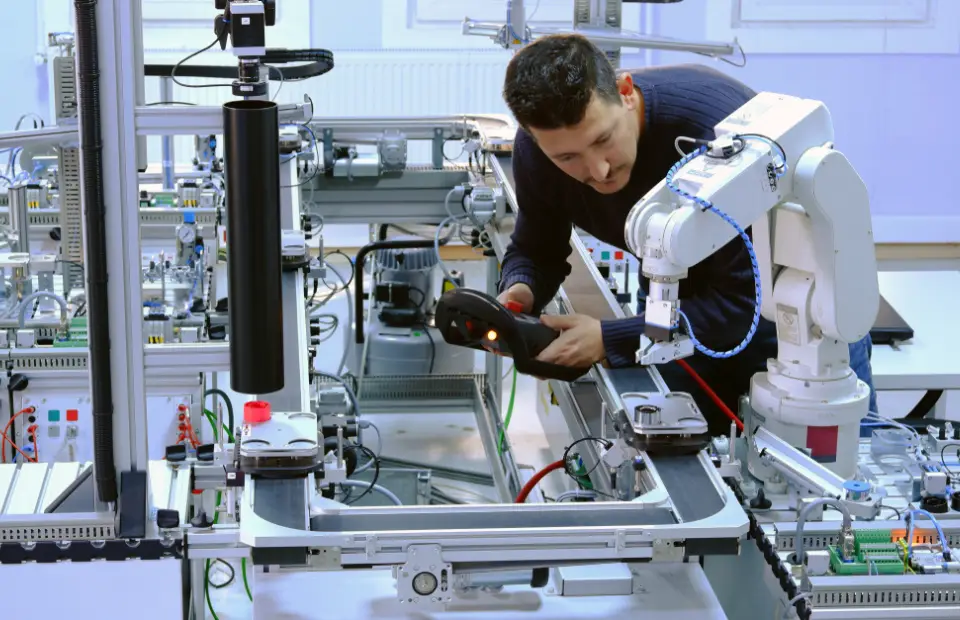

They are also called Cobots. Collaborative robots are designed to work with humans, facilitating cooperation in shared workspaces. They are just helpers. They incorporate sensors and safety features to ensure the well-being of human workers. Cobots are equipped with advanced safety features, including force and torque sensors, vision systems, and speed monitoring, allowing them to operate safely near humans.
| Features | Designed to work alongside humans, often with safety features like force sensing and power limitation. |
| Advantages | Safe collaboration with humans, easy to program, flexible deployment, smaller footprint. |
| Limitations | Lower payload compared to some industrial robots, may not be suitable for heavy-duty tasks, potential for reduced speed. |
Key Components of Industrial Robots
Industrial Robotics have these core components that increase their performance:
Manipulator Arms

Manipulator arms or robotic arms are the robotic limbs responsible for carrying out tasks. Their structure varies based on the type of robot. These arms are used for flexibility.
End effectors, or robot grippers, are attached to the manipulator arms to perform specific tasks. Grippers come in various designs, ranging from simple claws to specialized tools for tasks like welding or painting.
Sensors and Vision Systems
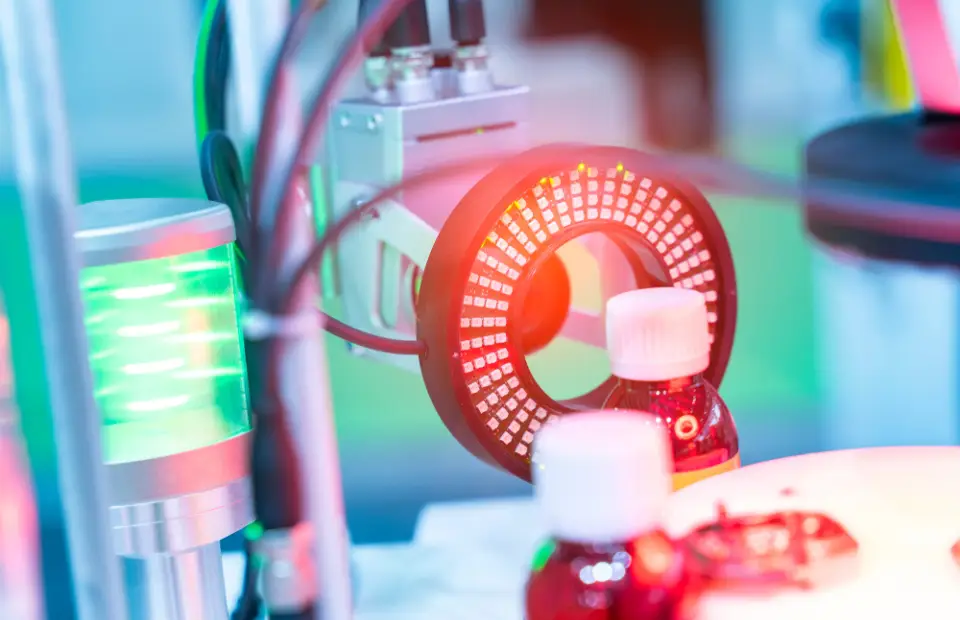

Sensors and vision systems are important components that enable robots to perceive their environment. This sensory input enhances the robot’s ability to adapt to changes and perform tasks with precision.
Vision systems, including cameras and other sensors, allow robots to identify and respond to objects in their surroundings, enabling them to perform tasks with a level of precision that was once thought impossible.
Control Systems
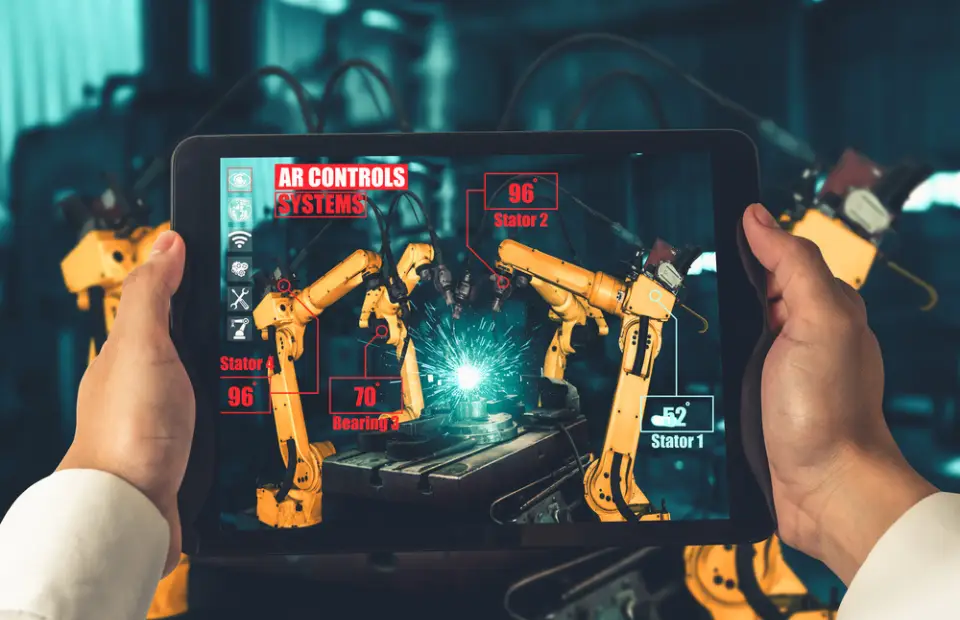

The control system is the main component of industrial robotics it is just like a brain. It controls all the movements and actions. Centralized control involves a single controller managing all robot functions, while decentralized control distributes control across multiple components.
Programming industrial robots involves specifying the sequence of movements and actions. Traditional programming methods include teaching pendant programming, while advanced robots can be programmed using offline programming software.
Advantages of Industrial Robotics

Increased Productivity
The use of robotics in industries increased productivity. Industrial robots operate at high speeds, significantly accelerating production processes. Their efficiency in performing repetitive tasks allows for continuous operation, contributing to increased overall productivity.
robots do not require breaks or rest, enabling continuous, 24/7 operation like humans. This contributes to a significant increase in output and a reduction in production time.
Precision and Accuracy
We have to accept that robots have a high precision rate and perform tasks with more accuracy. Robots consistently perform tasks with precision, reducing the margin of error in manufacturing. This precision is particularly crucial in industries where minute deviations can impact product quality. The ability of industrial robots to consistently deliver high-quality output and also increase it contributes to improved product quality and customer satisfaction.
Cost-Efficiency
No doubt initial investment in industrial robotics can be substantial, but the long-term savings in terms of increased productivity, reduced labor costs, and minimized errors justify the upfront expenses. Companies that invest in industrial automation often experience a rapid return on investment (ROI) as the benefits of increased efficiency and reduced operational costs become evident over time.
Conclusion
Industrial robots can help manufacturers by maximizing their production capacity and reducing operational costs. Industrial Robotics refers to the use of advanced robots in industrial states. I think no one doesn’t like comfort! so we use advanced technological machinery to reduce human efforts in industries. All complex tasks and operations are done by robotics which are done by humans traditionally in the past. As technology continues to advance, robotics become a more integral part of our lives. In the future, almost every industry use robotics to increase their productivity and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions on Industrial Robotics
How do industrial robots improve efficiency in manufacturing?
Industrial robots improve efficiency by operating at high speeds, performing repetitive tasks with precision, and enabling continuous 24/7 operation.
What safety measures are in place for collaborative robots?
Collaborative robots incorporate safety features such as force and torque sensors, vision systems, and speed monitoring to ensure safe interaction with human workers.
What role does artificial intelligence play in industrial robotics?
Artificial intelligence in industrial robotics enables machine learning, enhancing adaptability, decision-making, and the ability to handle complex tasks.
Are there any ethical considerations in the use of industrial robots?
Ethical considerations in the use of industrial robots include concerns about job displacement, worker safety, and the responsible development and use of AI in robotic systems.





