If you are a car lover like me, you probably know about Electric Vehicles. If not then don’t worry! read the whole article. Electric vehicles have become a trend these days. Many people prefer them over gasoline or petrol cars because of their amazing features and benefits. Charging cars and fuel cells are getting a lot of attention these days. Electric cars use electric motors rather than the petrol engine. You can never judge a car from the outside whether it is an electric car or a petrol car because there is no difference from the outside, the real magic is inside the car or in the engine. Mostly, electric cars are made of gasoline-powered cars so you can recognize them at first sight. But when you drive an electric car, it is more silent which makes a big difference.
In this article, we will discuss what EV vehicles are and how they work. We will also see their benefits and drawbacks in society.
- What Is an Electric Vehicle?
- How do Electric vehicles work?
- Physical Element of Electric Motor
- Difference between Engine and Motor
- Electric Vehicle Parts and Functions
- Types of Electric Vehicles
- How to Charge Electric Vehicles
- EV Vehicle Range
- Battery Capacity and kWh
- How Long does it take to Charge an EV Vehicle?
- Advantages of EV
- Drawbacks
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions on EV Vehicles
What Is an Electric Vehicle?

Electric Vehicles are also known as EVs. An electric vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that uses one or more electric motors for propulsion. EVs do not require an internal combustion engine to operate. It gains power from an electric motor rather than a gas engine. The electric motor gets the power from a controller which is connected to the accelerator of the car and gives energy according to the use of the accelerator pedal. EV vehicles store energy in batteries which are rechargeable from common electricity. EV vehicles move on roads without burning up fuel as well as not producing noise and harmful emissions.
How do Electric vehicles work?
EV vehicles are like automatic cars. Their working is the same as an automatic car working in forward, reversed mode. The power is converted into a battery from DC for the electric motor. The power supply from the controller is dependent on the accelerator pedal. When we press the accelerator it sends a signal to the controller which adjusts the vehicle speed with the change in frequency of AC power from the inverter to the motor. Then the motor connects and turns the rim of the wheels through the cog. The motor becomes an alternator when brakes are pressed and sends power back to the battery
Physical Element of Electric Motor
The Electric motor works on the principle of two main elements, the Stator and the Rotor
The electric motor creates a magnetic field using a current at the fixed part of the machine called the stator. Inside the stator, there is a rotating part called the rotor. The major difference between them is that the stator is static and the rotator is rotating; this is an easy way to remember these two elements of a motor.
In the Motor, the Stator creates a magnetic field using energy and then turns the rotor
Difference between Engine and Motor
A motor is a machine that converts energy into mechanical energy, while an engine does the same thing but uses thermal energy. Converting thermal energy into mechanical energy refers to combustion rather than electricity. In other words, an engine is a type of motor but a motor is not necessarily an engine. In Electric vehicles, mechanical energy is created from electricity. We use the “motor” word to describe the device through the electric vehicle moves
Electric Vehicle Parts and Functions
If you never drive an electric car, it’s simple to understand its main parts. For example, there are batteries instead of gas tanks and there are electric motors instead of engines. The amazing thing is that they have no tailpipe. But there are some more parts that you should understand if you have an EV car.
- Traction battery pack
- Power inverter
- Electric traction motor
- Power Electronics Controller
- Battery
- Charge port
- Dc Dc Converter
- Charger
- Transmission
Nowadays 3D printing has a great impact on the manufacturing industry so many parts of cars are made with the help of 3d printing.
1. Traction Battery Pack
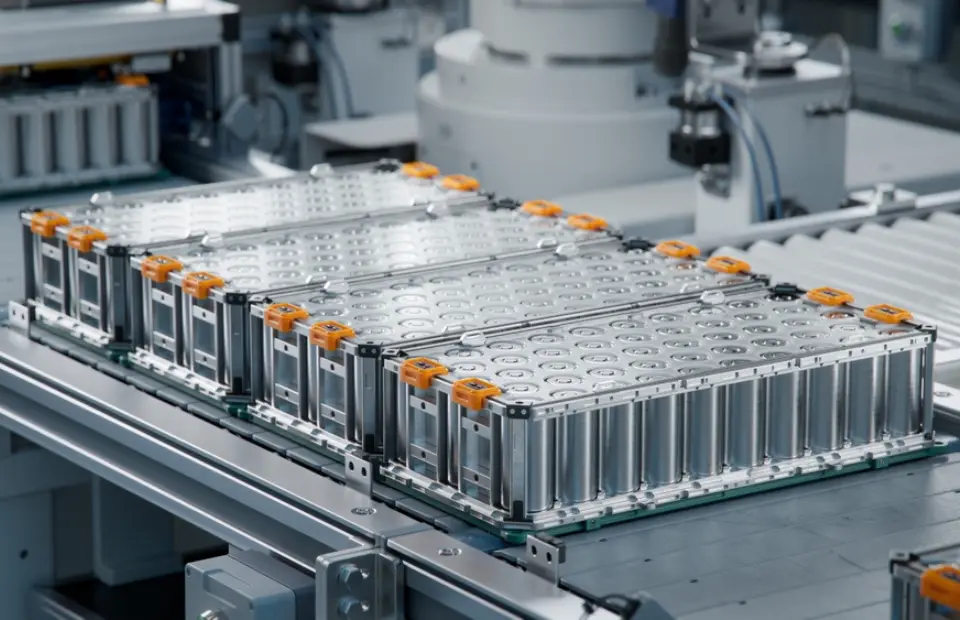
In an electric car, If the battery gets the signal from the controller, it transmits DC electrical energy to the inverter and then uses this energy to drive the motor. The rechargeable batteries are used in such a sequence called the Traction Battery Pack.
2. Power Inverter

The function of the inverter is to change the direct current into an alternating current on the battery. Electric motors use this alternating current. Moreover, the inverter of the electric car also can change the AC when regenerative breaking to DC and then use it to recharge the battery. In Some electric car models, the inverter is used which is mostly a bi-directional inverter.
3. Electric Traction Motor
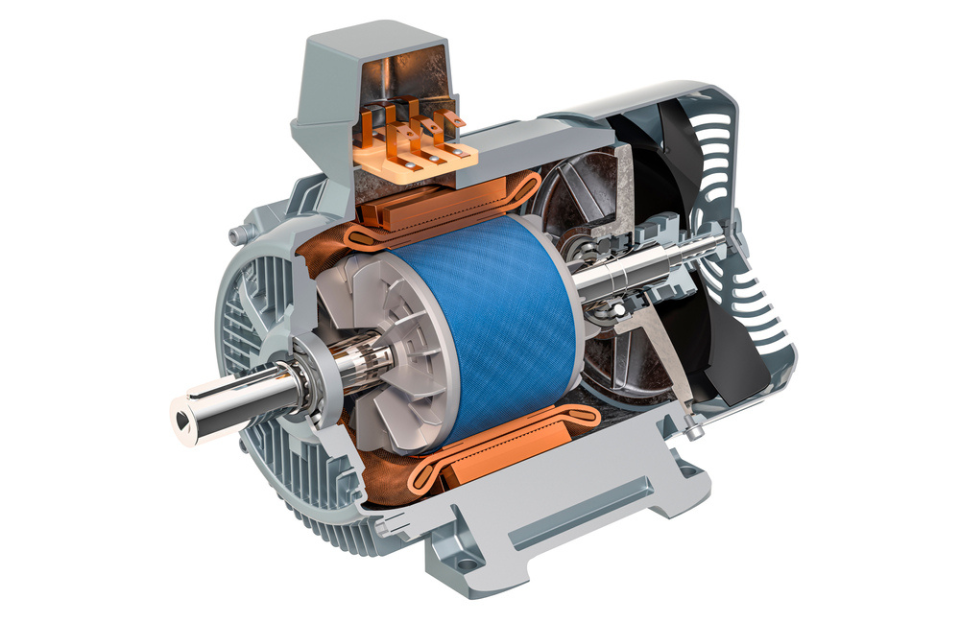
When the transmission and wheels are turned then the electric traction motors work using the power coming from the traction battery pack. Some vehicles use generator motors that perform two functions like derive and regeneration. In general, a Brushless DC motor is used as an electric motor in EVs
4. Power Electronics Controller
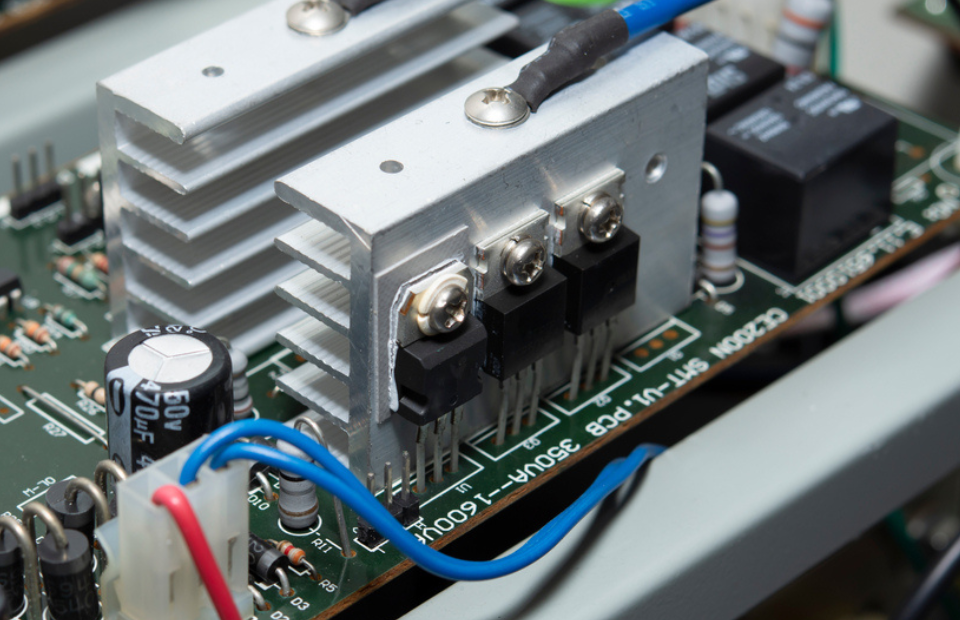
The combination of an Inverter and a converter recharges the battery pack of an Electric vehicle during regenerative braking and develops kinetic energy. The flow of energy from the battery is controlled with the help of a controller unit in Tandem (two things in one frame) with the combination of converter and inverter. In Some electric vehicles, The DC motor controller system is still used today to make it more cheap. However, today many electric vehicles use AC motor controller systems because they improve motor efficiency and lighter weight.
5. Battery(Auxiliary)

In BEV vehicles the auxiliary battery provides electricity to give power to the different components of the vehicle
6. Charge port
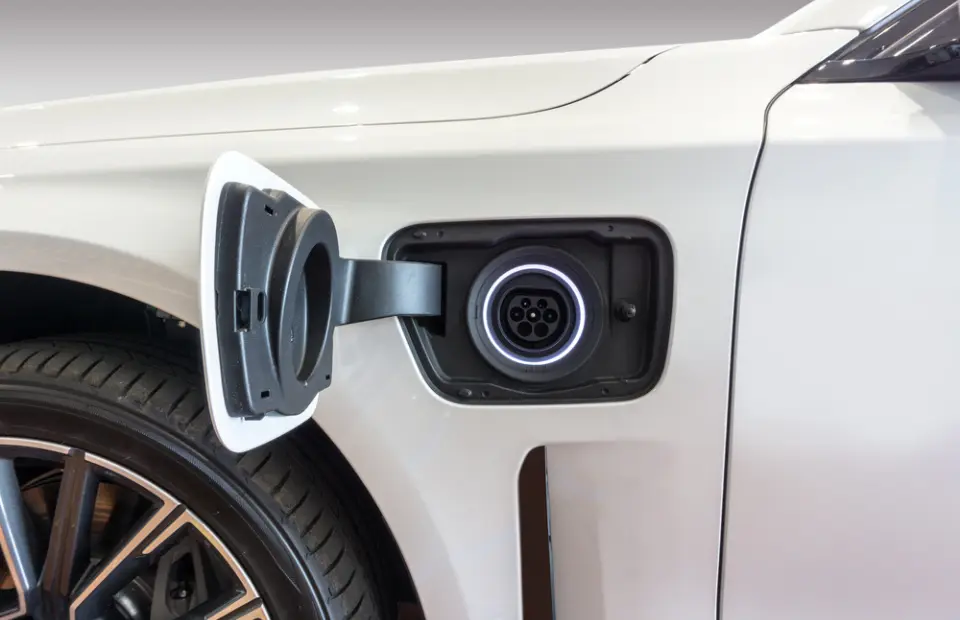

The charge port allows the electric vehicle to connect to an external power supply to charge the traction battery pack
7. Dc Dc Converter
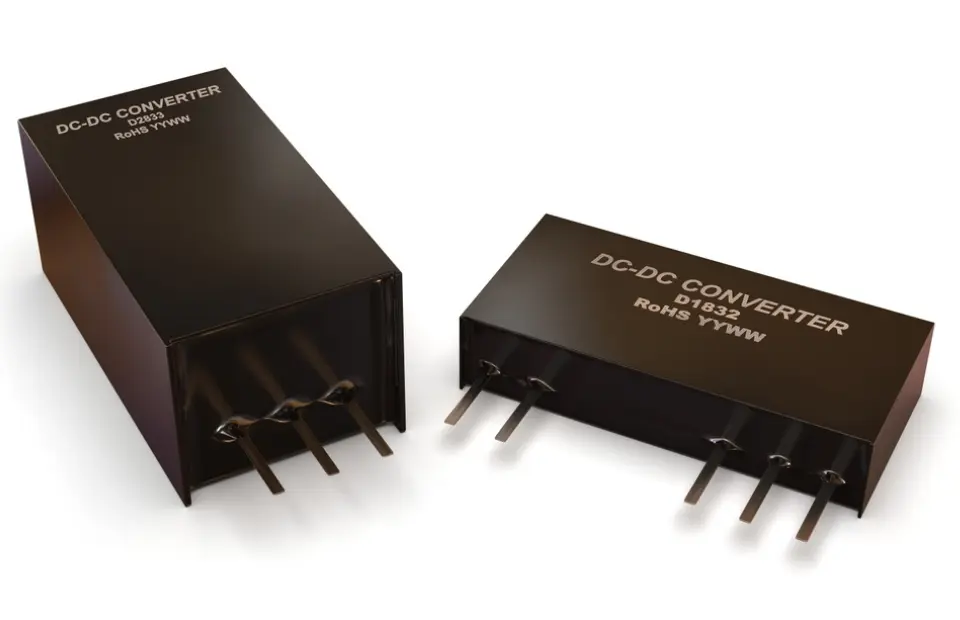

The device converts higher DC power from the traction battery pack to the lower DC voltage power which is needed to run the different components of electric vehicles and also recharge the auxiliary battery.
8. Charger

A charger is a device which is used to charge the batteries. it gets electricity from outside sources like utility grids or solar power plants. There are two types of Bev vehicle charger
Onboard charger: This charger is located and installed within the car.
Offboard charger: This charger is not located or installed in a car
9. Thermal Management In Electric Cars
Thermal system cooling, this system Maintains a proper operating temperature which is within the range of the engine’s electric motor which powers electronics and other components
10. Transmission (Electric)
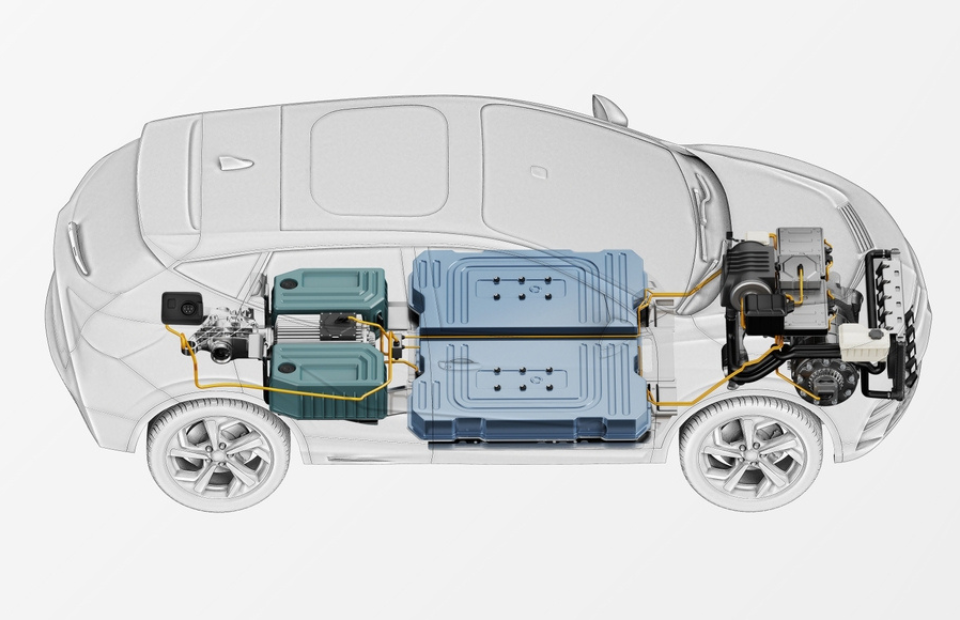

To drive the wheels the transmission transfers mechanical power from the electric traction motor.
Types of Electric Vehicles
There are four types of electric vehicles in which electric cars are available:
- Battery Electric vehicle (BEV)
- Hybrid electric vehicle(HEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid electric vehicle(PHEV)
- Fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV)
1. Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
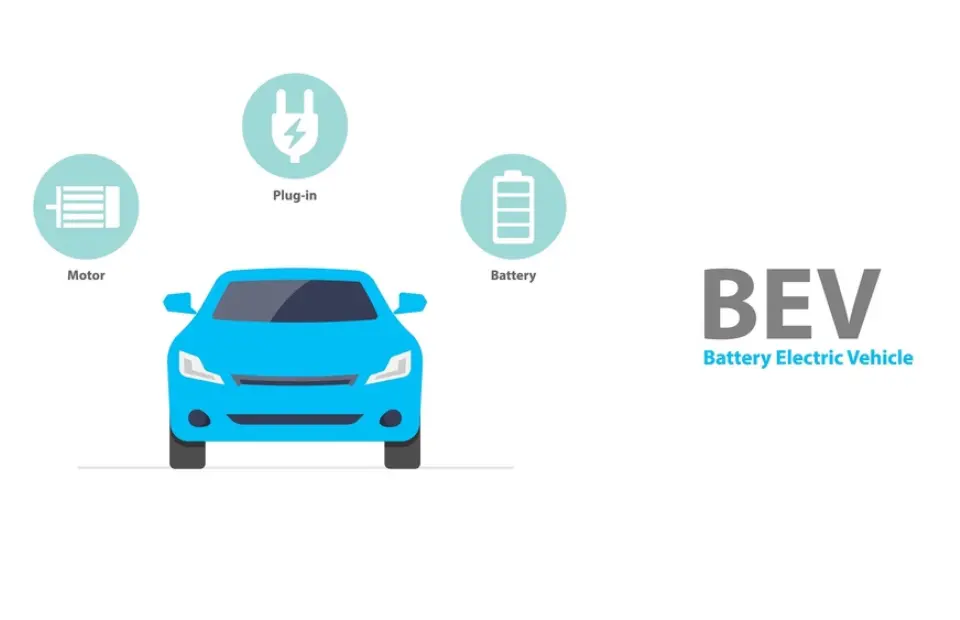
It is also called an all-electric vehicle because this is entirely run on battery. Electricity is stored in a large battery pack which is charged by plugging into the electricity grid in return the battery pack provides power to one or more electric motors to run the electric car
Examples of BEVS
- Volkswagen e-Golf
- Tesla Model 3
- BMW i3
- Chevy Bolt
- Nissan Leaf
2. Hybrid electric vehicle(HEV)

They are often called standard hybrid or parallel hybrid vehicles. Hybrid Electric vehicles have both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor. In these vehicles the internal combustion engine gets energy from the fuel Gasoline and the fuel of other types on the other hand the motor gets power from the battery. Together, the gasoline engine and electric motor drive the transmission which drives the wheels.
The main difference between a hybrid vehicle and an electric vehicle is that the battery in a hybrid can only be charged by an Engine( Internal Combustion). There is no charging port so the battery cannot be recharged from outside of the system
Example of Hybrid Vehicles
- Honda Civic Hybrid
- Toyota Prius Hybrid
- Toyota Camry Hybrid
3. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV)
It is just like a hybrid vehicle with both an IC engine and a motor. This type of vehicle provides the fuel option. They get power from conventional fuel such as gasoline or an alternative fuel such as
biodiesel and rechargeable battery pack. The battery charges electrically by plugging into an electrical outlet or electric vehicle charging station. Plug-in hybrid vehicles run in two modes, All electric mode in which the motor and battery provide all the energy to the car. The second one is hybrid mode in which both electricity and gasoline provide the energy. Some Plug vehicles cover more than 70 miles of distance by only depending on electricity.
Examples of Plug-in electric Vehicles
- Porsche Cayenne SE Hybrid
- Audi A3 e-tron
- Ford C-Max Energi
- Mercedes c350e
4. Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
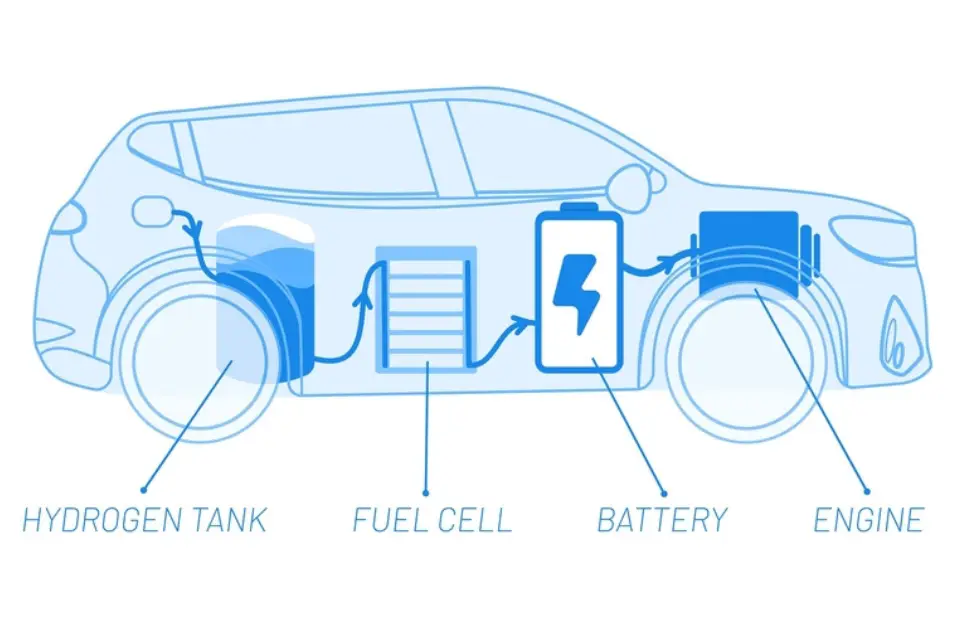
Fuel-cell electric vehicles are also known as zero-emission vehicles. It employs fuel cell technology to generate the required electricity to run the vehicle. In Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle. The chemical energy of the fuel is directly converted into electric energy.
Examples of fuel-cell electric vehicles
- Toyota Mirai
- Hyundai Tucson
- Riversimple Rasa
- Hyundai Clarity Fuel Cell
How to Charge Electric Vehicles
You can charge the electric vehicle by plugging it into a public charging station or with the help of a home charger. But to get the best deal for home charging it is important to get the right EV electricity tariff (The rate at which electrical energy is supplied to a consumer) so in this way you can spend less money on charging and save more on your bill.
EV Vehicle Range
How far can you travel on a full charge? It depends on the vehicle. Each model of EV has a different range according to battery size and efficiency.
Volkswagen E-golf Range
Battery – 24.2 kWh
Range- 125 miles (201km)
Hyundai Kona Electric
Battery – 64 kWh
Range – 250 miles (402 km)
Jaguar I- Pace
Battery – 90 kWh
Range – 292 miles (470 km)
Battery Capacity and kWh
Kilowatts is the unit of power, how much power does a device need to work?
A kilowatt-hour is a unit of energy, how much energy has been used?
For example :
- A 100-watt light bulb uses 0.1 kilowatts each hour:
100W light bulb = 0.1 kw / hr
- An average home Consumes three thousand and one hundred kilowatt hours of energy per year:
3100 kWh energy/year
- An electric car consumes an average of 2000 kilowatt hours of energy per year:
2000 kWh energy/year
How Long does it take to Charge an EV Vehicle?
There are three electric vehicle charging speeds
Slow charging: It is typically rated up to three kilowatts and is often used to charge overnight or at the workplace charging time takes up to eight to ten hours
Fast charging: It is typically rated at either seven kilowatts or 22 kilowatts and tends to be installed in car parks, supermarkets, leisure centres and houses with off-street parking charging time that takes up to three to four hours.
Rapid charging: It is typically rated from 43 kilowatts only compatible with EVs that have rapid charging capability. Charging time takes up to 30 to 60 minutes
Advantages of EV
1. Easier on the Environment
Electric vehicles have no combustion system or exhaust system so they don’t have poisonous emissions. By using electric cars we can clean the air and have a healthier planet
2. Electricity is Cheaper than Gasoline
Electricity is comparatively less expensive than other fuels (Gasoline or diesel). you can also use solar panels to charge your electric car as well and you can also use this electricity for your home.
3. Low Maintenance Need
Electric cars don’t use oil for operating so they don’t require any oil changes also they don’t have many components that need to be replaced or repaired compared to gas-powered vehicles.
4. High Quality Performance
Electric cars are popular for operating smoothly and quietly because there is no exhaust system. They are more quieter than conventional gas engines reducing noise pollution and making the drive more comfortable. Electric motors also respond much faster than mechanical Engines.
5. More Convenient
Recharging an electric vehicle is easy and the best thing is you don’t need to run to the fuel station to recharge your car even you can charge your electric car in your house with the normal socket.
Drawbacks
1. Finding a Charging Station is Challenging
The main drawback of an electric car is to find a charging station. No doubt you can charge your electric car in your house but it isn’t easy to find a charging station when you drive outside the city or on a long-distance road trip.
2. Changing Can Take a While
To add gas to the fuel tank in a car it’s hardly takes 10 to 15 minutes but recharging an electric car can take more time. If the battery is empty it can take up to 15 to 20 hours to charge the full battery using a normal outlet. An even faster charging station will take 30 minutes to recharge an electric car up to 80%.
3. Limited Driving Range
Driving with an electric vehicle is limited. Like you have to charge a full battery if you want to cover a long distance. Imagine you go for a long drive and your battery runs out in the middle of the road and you have no charging station near. It’s really terrifying!
4. High Initial Cost
The upfront price of most electric cars is much higher than the gas-powered vehicles. Even the most affordable electric car models from 30k dollars to 40k dollars range while luxury models 80k dollars or more.
Conclusion
No Doubt Electric cars change our lifestyle completely but it is more expensive because they are new in the market we hope as time passes electric cars become normal and cheaper than everyone buys them easily!
Frequently Asked Questions on EV Vehicles
How do electric vehicles work?
Electric vehicles use electricity stored in batteries to power an electric motor, which then drives the vehicle's wheels. The batteries are recharged by plugging the vehicle into an electric power source, such as a charging station or wall outlet.
How far can electric vehicles travel on a single charge?
The range of electric vehicles varies depending on factors such as battery size, vehicle efficiency, driving habits, and weather conditions. Modern EVs typically have a range of anywhere from 100 to over 300 miles on a single charge.
Are electric vehicles environmentally friendly?
Yes, electric vehicles are generally considered more environmentally friendly than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles because they produce zero tailpipe emissions when powered solely by electricity. However, the overall environmental impact depends on factors such as the source of electricity used for charging.





